According to the EPA, “the National Waste Minimization Program supports efforts that promote a more sustainable society, reduce the amounts of waste generated, and lower the toxicity and persistence of wastes that are generated.” The program focuses on 31 separate “priority chemicals” found in many of our nation’s wastes and products. The primary focus is on eliminating or reducing the quantity of these chemicals that are produced with a secondary focus on recycling them when reduction or elimination cannot be achieved.
There are a few different tools and methods that can be used to aid in the reduction and elimination of these wastes including, “lean manufacturing, energy recovery, Environmental Management Systems (EMS), and green chemistry.” More information about each of these methods can be found on the Heritage website.
A major player in the minimization game is the hazardous waste reduction plan. A hazardous waste reduction plan (often referred to as a waste minimization plan) is required for all hazardous waste generators. General requirements include:
- Corporate policy statement of support for pollution prevention
- Description of your pollution prevention planning team(s) makeup, authority, and responsibility
- Description of how all of the groups (production, laboratory, maintenance, shipping, marketing, engineering, and others) will work together to reduce waste production and energy consumption
- Plan for publicizing and gaining company-wide support for the pollution prevention program
- Plan for communicating the successes and failures of pollution prevention programs within your company
- Description of the processes that produce, use, or release hazardous or toxic materials, including clear definition of the amounts and types of substances, materials, and products under consideration
- List of treatment, disposal, and recycling facilities and transporters currently used
- Preliminary review of the cost of pollution control and waste disposal
- Description of current and past pollution prevention activities at your facility
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of past and ongoing pollution prevention activities
- Criteria for prioritizing candidate facilities, processes, and streams for pollution prevention projects
These Hazardous Waste Reduction Plans should be updated annually and there should always be a copy onsite. Additionally, while the points above cover national requirements, many states have additional criteria that must be met. By making sure to keep this plan up-to-date and available you can help prevent EPA violations for your company.
More News From Heritage
-
Published Articles 8/2/22
How Safety, Maintenance, and Reliability Are Intertwined
VP of Health and Safety Jim Mangas discusses the importance of plant safety, maintenance, and reliability (featured in BIC Magazine July/Aug '22)
-
Blogs 7/28/22
Spotlighting Our Environmental Interns
Highlighting some of the wonderful interns we have at Heritage this year!
-
Blogs 7/11/22
Turning Hazardous Waste into an Alternative Fuel
In this blog we walk you through the process of fuel blending, where we can turn hazardous waste materials into a viable alternative fuel source.
-
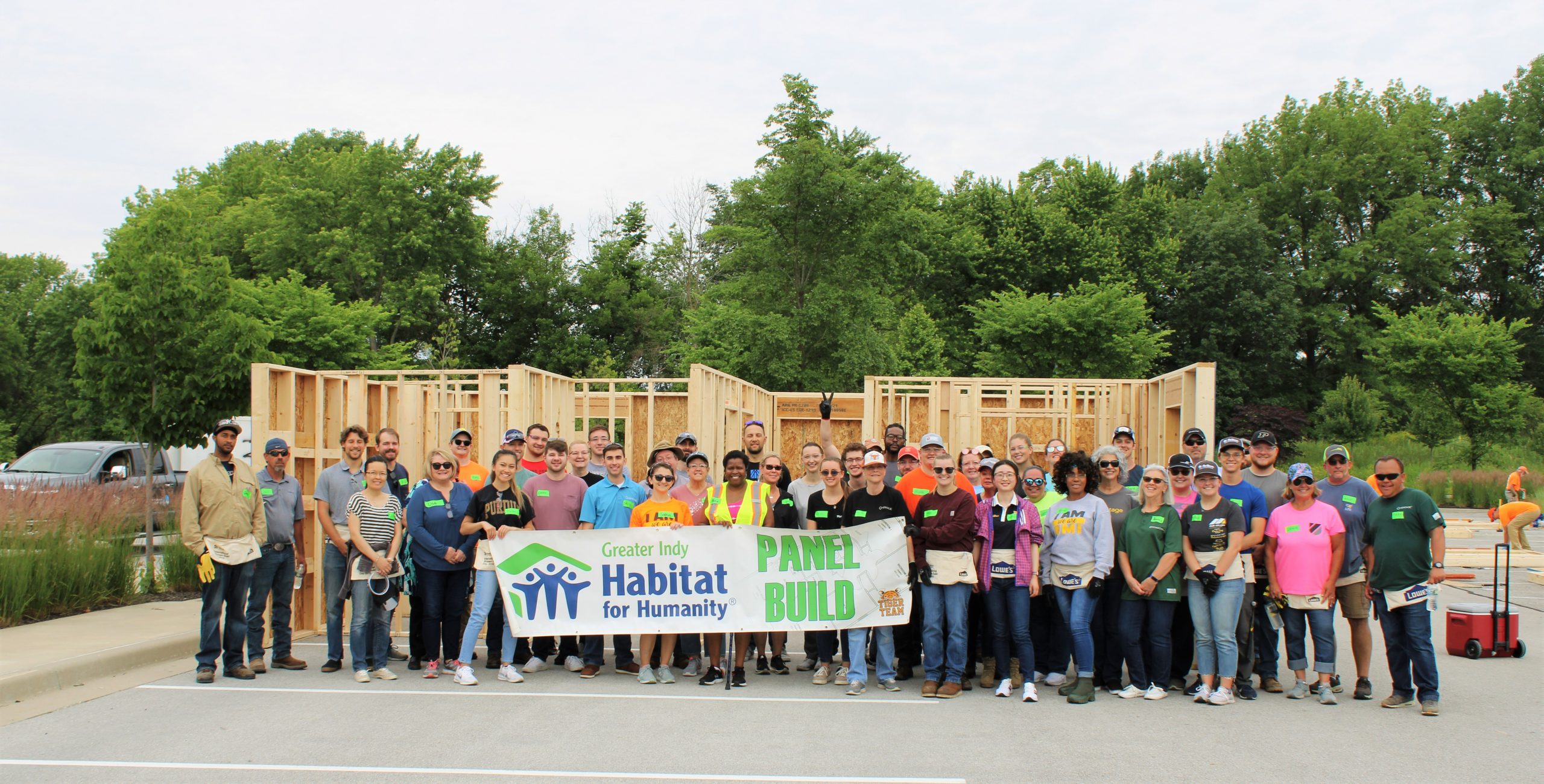
Community News 6/15/22
2022 Habitat for Humanity Build
Our 12th annual Habitat for Humanity Build
-
Blogs 4/13/22
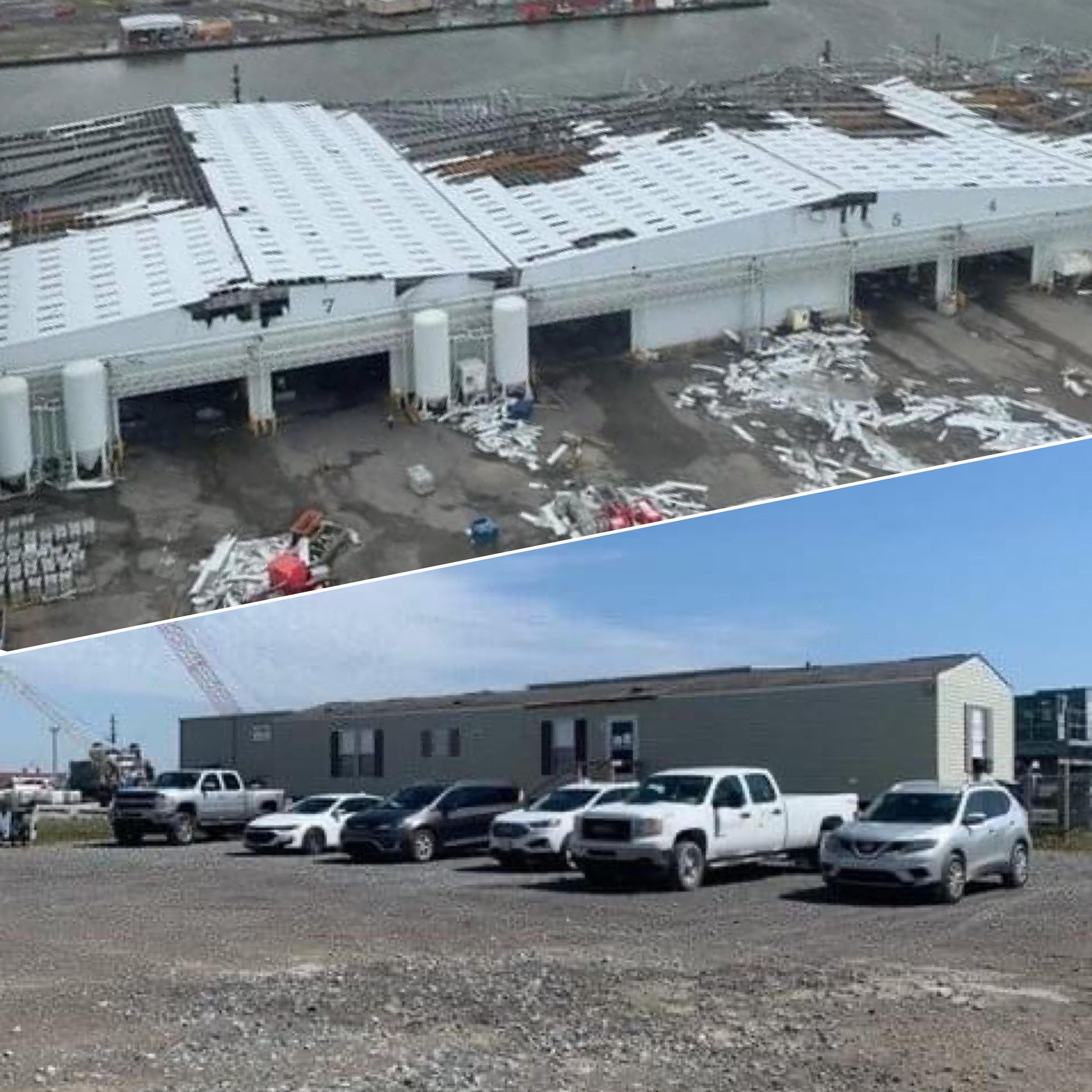
After Hurricane Ida, Our Port Fourchon Office Rebuilds
On August 28th, 2021, the Louisiana coast was battered by Hurricane Ida. This included our Port Fourchon Service Center, where the devastating hurrica
-
Community News 4/7/22
Heritage readies for Earth Day HHW collection in East Liverpool
Heritage Thermal Services is pleased to announce that its collection of household hazardous wastes for the East Liverpool area returns for 2022.
-
Published Articles 4/2/22
The Impact of Changing Conditions
VP of Health and Safety Jim Mangas discusses preparedness for unexpected conditions during a project. (featured in BIC Magazine March/April '22)
-
Blogs 3/11/22
International Women’s Week Spotlight – Rachel McGrogan
Rachel McGrogan speaks about her time as a Lab Chemist at Heritage.